

Since rolling mill rolls are used to process materials (steel) with temperatures of over 1,000°C, they are subject to surface damage (wear and roughening).
For this reason, to maintain product quality, after a certain period elapses, rolling mill rolls must be prepared by repeatedly grinding down the surface of the roll to ensure surface quality.
Rolls may also be damaged due to rolling problems that occur during use.
Our Technical Services Department provides prompt, attentive after-sales service from delivery through to disposal to ensure that all customers can use their rolls with peace of mind.
To ensure that customers' mills operate efficiently, in addition to improving the quality of rolled steel, it is important to consider and address both the manufacturing technology of the rolls and the technology for using the rolls (rolling operating conditions).
By utilizing the knowledge and experience we have cultivated over many years as a roll manufacturer of Nippon Steel Corporation, which has high technical capabilities as well as the strengths of our "single-location, integrated production system," we provide technical support and suggestions from a variety of perspectives to satisfy our customers while working to improve roll quality and to develop high-performance rolls.
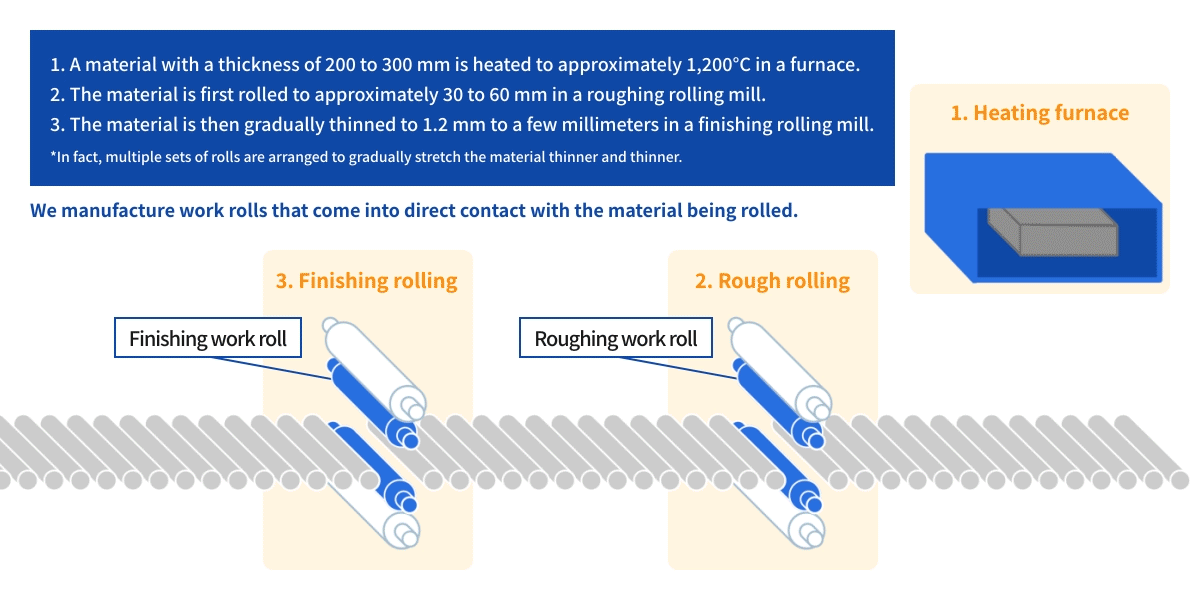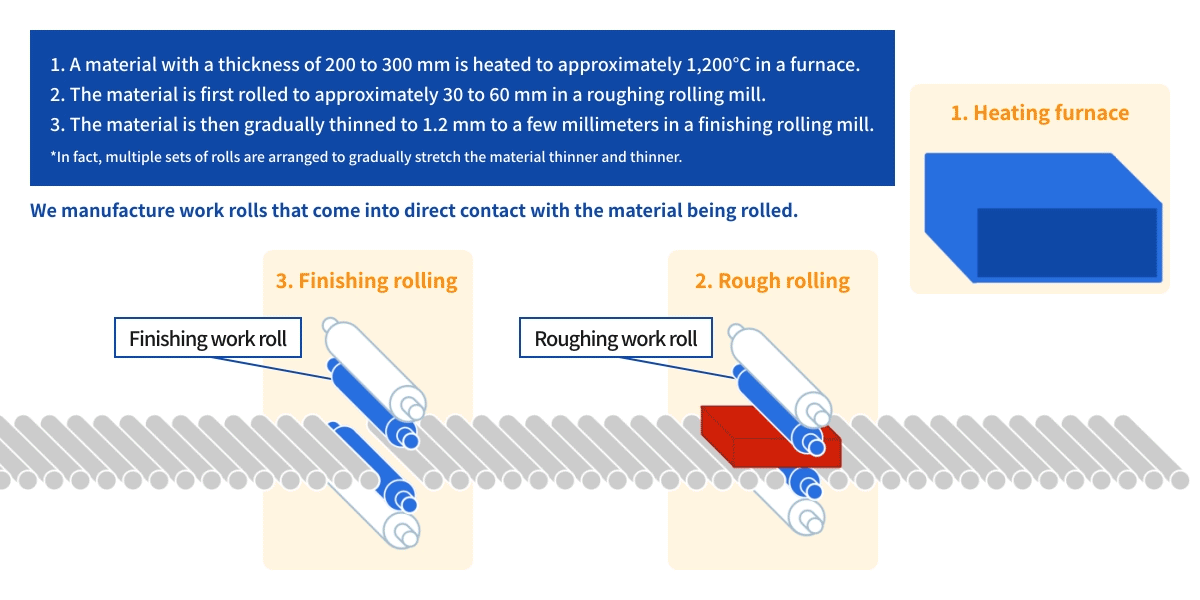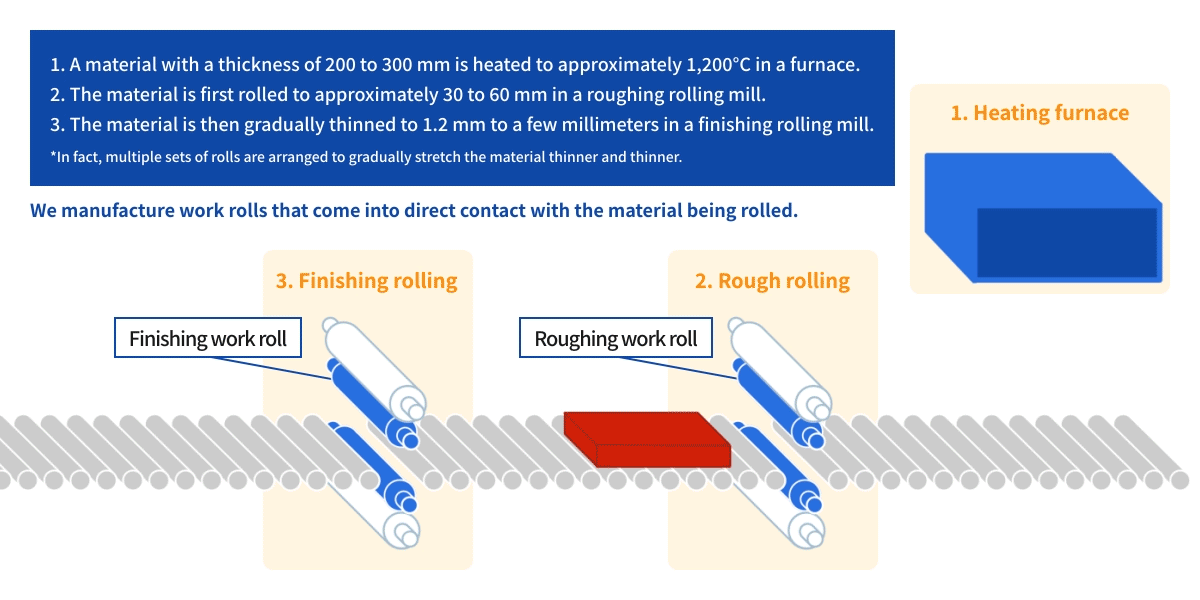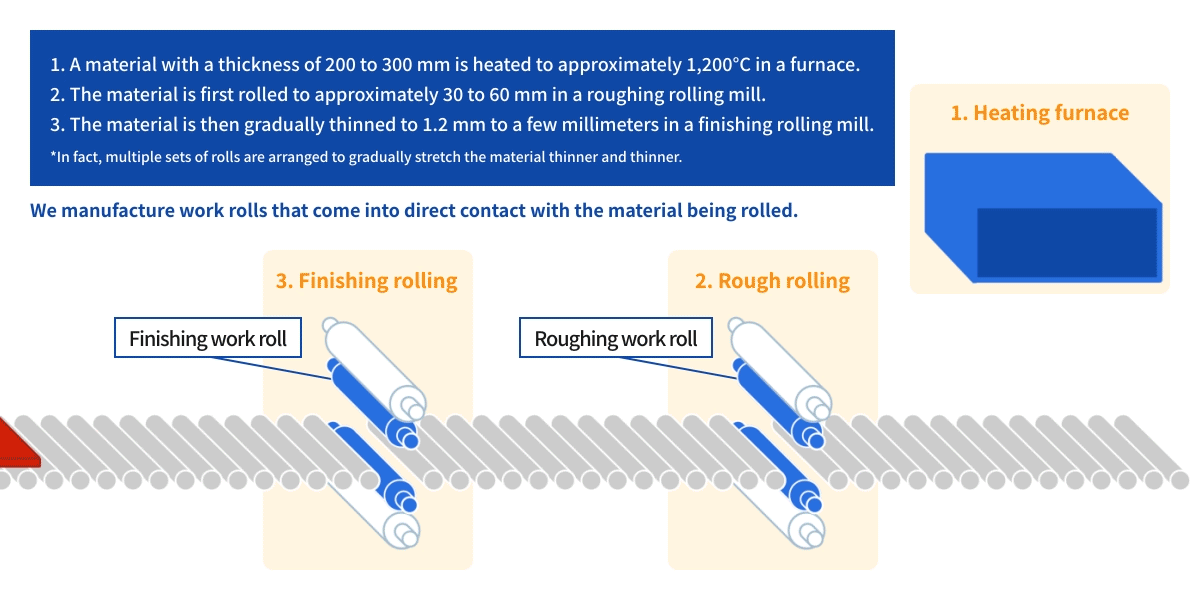
Watch a video of the actual rolling process using a rolling mill.
(From the Nippon Steel Corporation website)
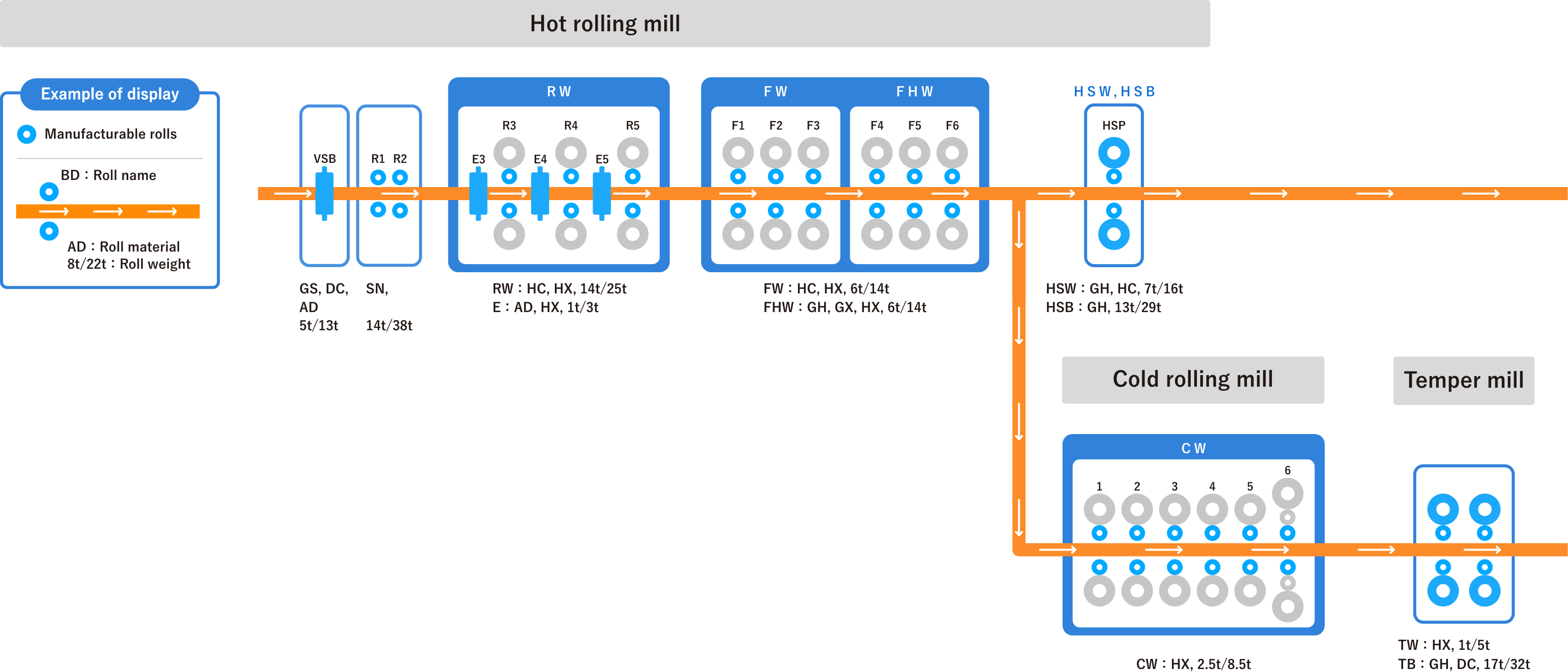
Hot Rolling Rolls

Hot strip mills had been installed the shape control function earlier than other types of mills.
The most sought-after roll material specification was the longevity.
Roughing Work Rolls
Double-type roughing work roll
Double-type roughing work rolls require good slip resistance, heat crack resistance, and wear resistance. To meet these requirements, we recommend a one-piece roll made of special cast steel with special heat treatment. Such rolls also have high strength and high performance comparable to that of forged rolls.
Quadruple-type roughing work roll
Due to the high performance of finishing work rolls, the same heat cracking resistance, surface roughening resistance, and wear resistance as that of the rolls used in the first stage of finishing rolling are required for quadruple-type roughing work rolls. To this end, we use a one-piece high-speed steel (HSS) roll made by centrifugal casting.
Edger roll
Extending the service lives of edger rolls, for which a long time is required to change rolls, significantly improves the productivity of the entire hot rolling line. This is achieved by using sleeve-type centrifugal casting HSS rolls, which have a service life several times longer than conventional materials and are becoming very popular.
Finishing Work Rolls
Upstream work roll
On the upstream stand, the work roll surface would conventionally form a black skin, which tended to cause surface roughening due to the peeling of the black skin in strips (banding). HSS rolls have rapidly become popular as rolls made of a material that has high wear resistance without relying on black skin formation. However, Nippon Steel Rolls Corporation is working to research and develop as well as manufacture an optimal roll material based on an understanding of the rolling conditions and wear conditions of the roll surface, including black skin formation.
The CPC HSS roll, which we successfully developed in a world first in 1990, still has the best service record in the industry thanks to our tireless research and development.
Downstream work roll
The downstream stand requires rolls that are highly resistant to wear and also resistant to rolling accidents as well as rolls with a good surface finish on the rolled material. Nippon Steel Rolls Corporation's Super Nickel Grain is a roll that meets these needs, and its applications are rapidly expanding as a roll that combines high wear resistance with surface stability.
In addition, as the rolling unit is expanded, applications of CPC HSS rolls and centrifugal casting HSS rolls, which are more suitable for mass rolling, are also expanding.
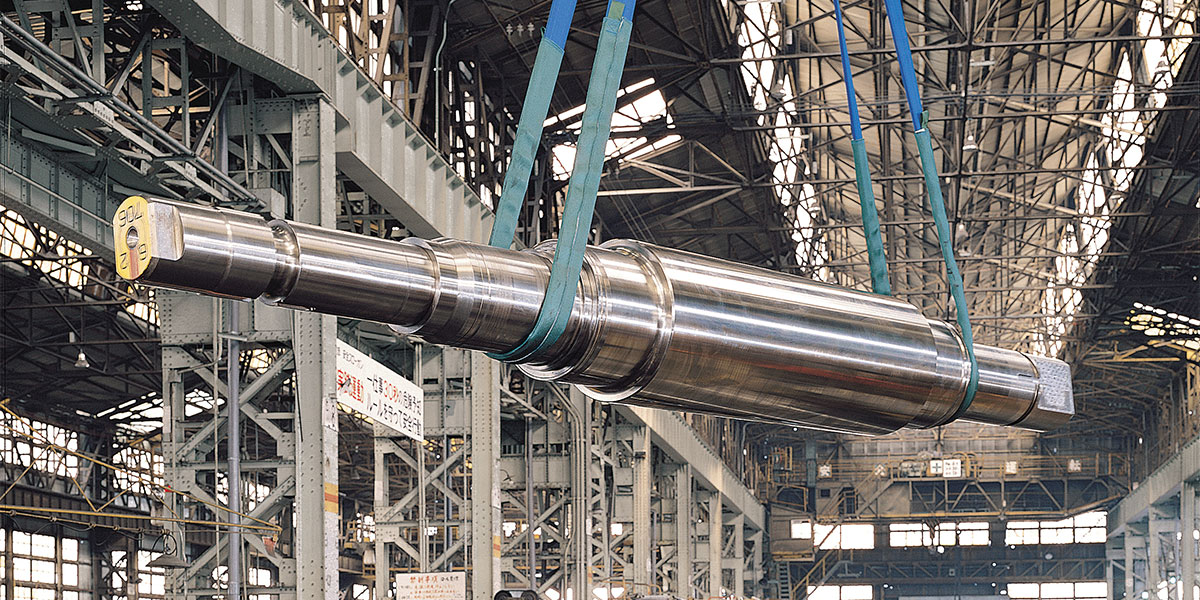
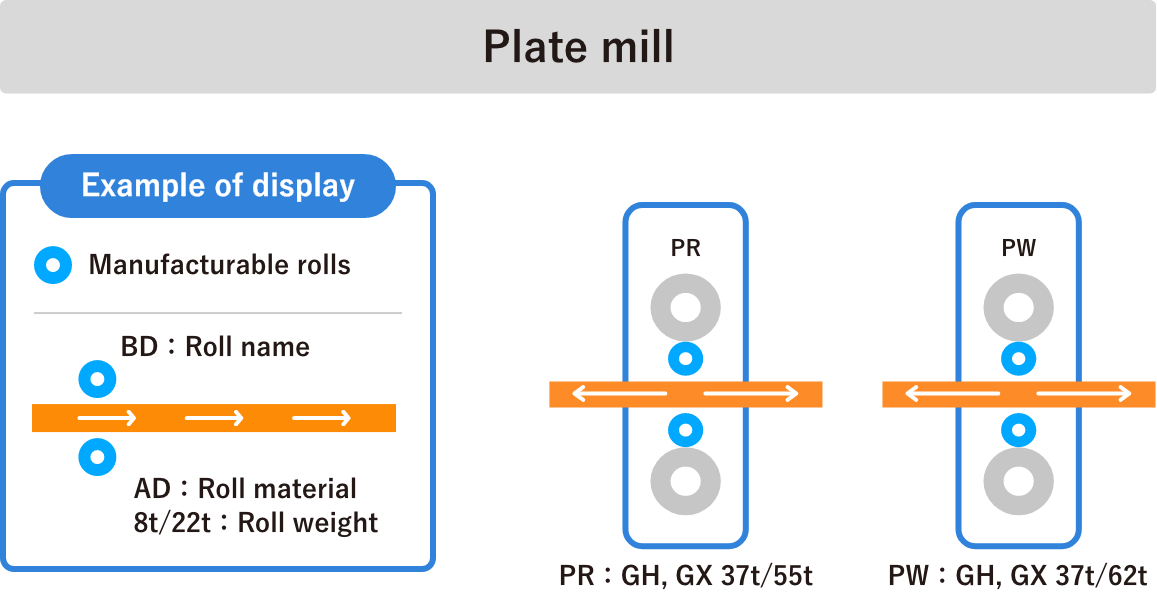
Steel-plate Rolls

Recent advances in plate rolling technology have introduced new rolling conditions that are more demanding than ever before, with the aim of achieving a finer grain size through controlled rolling in addition to conventional shape control functions.
In addition, in times of increased demand for ships, it became necessary to maximize production volume. To meet the needs of plate mills, plate work rolls must have improved toughness, wear resistance, surface roughening resistance, and accident resistance.
In addition, with the widespread use of wide rolling mills, steel plate rolls longer than 5 m have become common. We offer rolls that meet these requirements.
In roughing mills, rolls are used for longer periods than in finishing mills, so we recommend nickel grain as a highly reliable material due to low heat cracking, but super nickel grain, which has improved wear resistance, is also popular. We also manufacture high chromium rolls according to customer requirements.
Finishing mills require rolls that are tough, highly wear resistant, have a beautiful surface finish, and are less likely to break due to accidents such as peeling of the chill layer.
For this requirement, our nickel grain rolls and super nickel grain rolls, which have even finer structures and higher hardness than those for roughing mills, are popular.
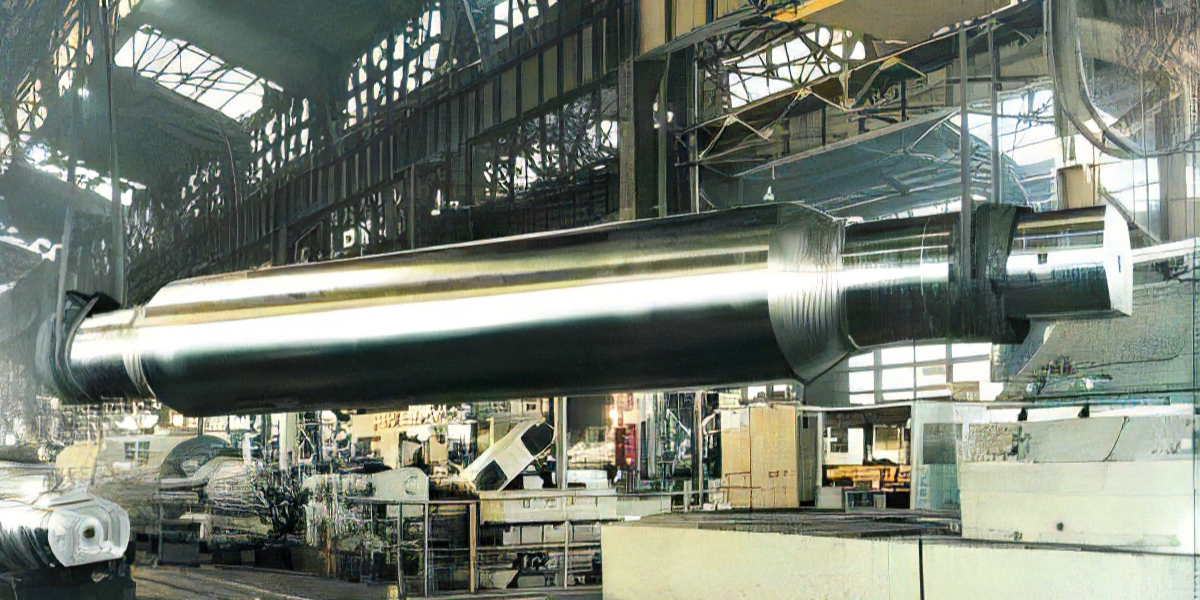
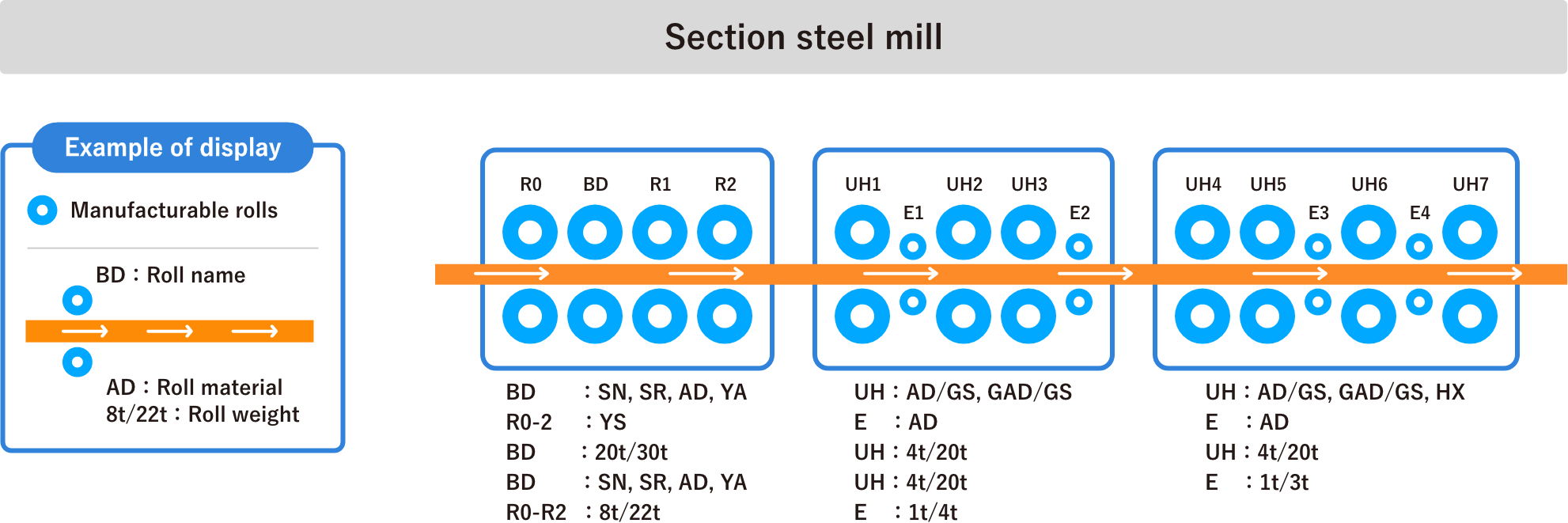
Section Steel Rolls

Breakdown roll
In breakdown mills, where the material taken from the heating furnace is first rolled, long rolls with multiple calibers are used. The forces acting on the rolls are analyzed based on the rolling conditions, such as rolling type, rolling load, and caliber type, and the optimum material is then selected. Forged adamite rolls that combine wear resistance, surface roughening resistance, toughness, and bite capability are used.
Double-type roughing and finishing roll
Rolls used in the rolling of steel sheet piles, rails, and angle steel must be strong enough to resist breakage and damage to the body from the bottom of the caliber, and must also resist sliding wear and seizure between the steel material and the caliber sidewall. We recommend an optimal material, such as adamite or forged adamite, based on the rolling load and wear of the caliber.
Universal mill roll
For roughing and finishing of H-shaped steel, adamite sleeve roll assembly type rolls, which were developed when the universal mill at Nippon Steel Corporation's Sakai Works started operation in 1962, are still the mainstream technology.In recent years, use of graphite adamite, which combines wear resistance with seizure resistance, and centrifugal casting high-speed steel (HSS), which has dramatically improved wear resistance, has increased for horizontal rolls. For vertical rolls, we use the most suitable alloy adamite or graphite adamite depending on the stress generated.
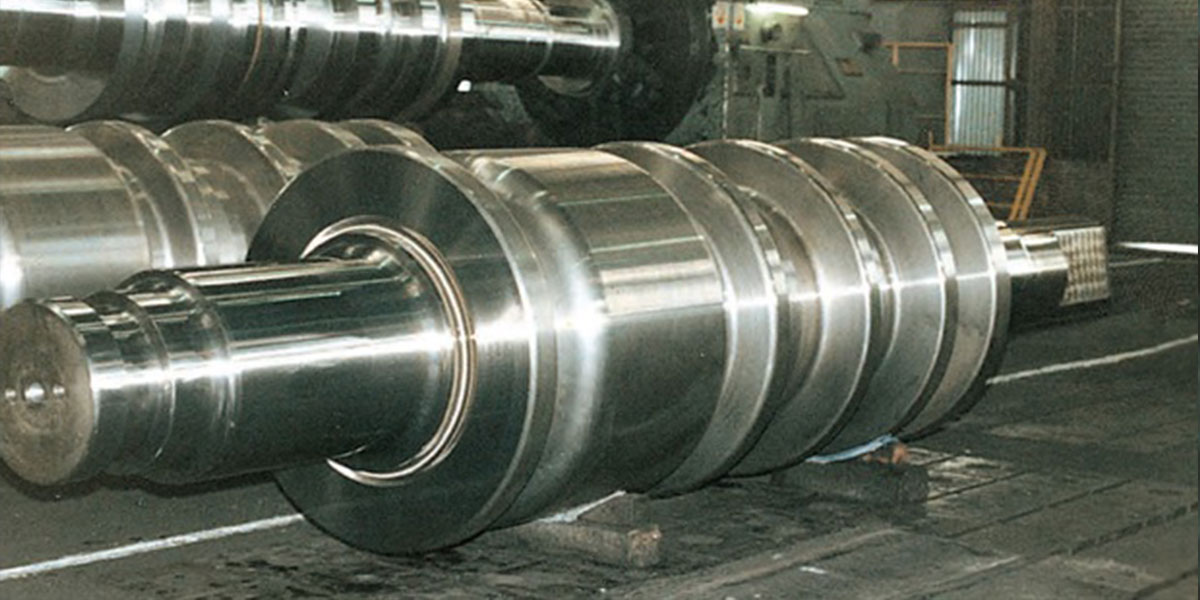
Blooming and Billet Rolls
In the case of high carbon steels and special steels, semi-finished billets are sometimes produced by blooming.
Nippon Steel Rolls Corporation provides rolls suitable for such rolling processes.
In blooming and billet mills, forged adamite rolls, which combine good bite and wear resistance of the caliber sidewall with high toughness, are widely used.
On the other hand, in slab mills, which are downstream of continuous casting to supply semi-finished slabs of various shapes for plate and hot rolling, highly reliable rolls that can be used with confidence for long periods are required. Special cast steel rolls with both strength and wear resistance provided by special heat treatment are used for rolls without calibers, and high-alloy adamite rolls with wear resistance are used for rolls with calibers.
here
